
Welcome to the ASU Core Facilities Newsletter. We are ready to support all your research goals. Please follow our LinkedIn page for additional resources and community information.
News
ASU spinout company, Swift Coat, blasts off

Reuniting humanity with a place untouched for over 50 years: the moon. NASA's Artemis missions aim to establish a moon base camp and orbiting spaceship, Gateway. Astronauts will utilize the state-of-the-art Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit (xEMU) spacesuit, featuring advancements like an anti-fogging helmet. ASU's Professor Zachary Holman and alumnus Peter Firth, founders of Swift Coat, have been chosen by NASA to develop a specialized coating ensuring clear vision for xEMU wearers. Swift Coat got it's start using equipment in the Core Research Facilities.
Learn about Swift Coat's contributions to NASA’s new space helmet.
ASU's Sol ranks among top performing supercomputers globally

ASU's Sol supercomputer secures top rankings on the global stage, surpassing prestigious institutions like Harvard, NYU, and Johns Hopkins on the TOP500 list—a ranking of the world's fastest supercomputers. Furthermore, Sol shines as a top-performing research supercomputer on the IO500 list.
ASU Research Computing has downloaded various open-source large language models (e.g., Falcon, LlaMa, Alpaca, MPT, etc.), harnessing Sol's power for tasks like inference and fine-tuning. For additional details or to request a demo of these applications, please visit us at https://rto.asu.edu/request-help.
Read more about this achievement.
The U.S. is about to open a new window into Earth's Mysterious Insides, with help from ASU

Step into the realm of high-pressure research at Dan Shim lab at ASU, where scientists simulate extreme planetary conditions. These explosive experiments provide insights into deep planetary realms, tackling fundamental questions about Earth's habitability, the origins of life and the enigmatic forces shaping our existence. This research was aided by instrumentation in our Eyring Materials Center Core Facility.
Learn more about these extraordinary experiments.
New EMC Equipment
This summer, the Eyring Materials Center has welcomed several new instruments into their facilities. Learn more about those instruments, their application and watch exciting videos of their uncratings here.
The Thermo Fisher Scientific Talos F200i (S)TEM will send electrons through your sample to image it at atomic resolution. Its dual X-ray detector will provide rapid elemental composition. The advanced segmented detector will also further inform the sample image. The addition of the Merlin detector will also allow us to use the instrument for 4D imaging, giving not only a picture of the samples but additional structural information at each point on the image.
The Xenocs Xeuss 3.0 is a versatile diffractometer primarily optimized to provide information about samples in the nanometer to micrometer scale. It is used to study solutions, suspensions and solids in various environments and sample conditions such as heating and cooling, range of relative humidity and tension to see changes in polymers as a function of strain. The robot arm can automatically process large series of solutions by cleaning the sample tube between each loading in the BioCube biocube.
The STOE STADI P is a dual transmission diffractometer with one side used exclusively to study the low and medium range order in semi-crystalline and amorphous materials at both ambient temperature, low temperatures, and high temperatures (-170°C to 1500°C). The other diffractometer is used for ambient condition measurement of powders, and in operando coin cell and pouch cell batteries.
The Rigaku SmartLab is a high-resolution diffractometer use to characterize epitaxial and polycrystalline thin films. We can use it to determine layer composition and relaxation in semiconductors, solar cells and LED. This new diffractometer talks to you as it guides your through the setup process to ensure you get the optimal measurement setup.
Publications
Three-Dimensional images reveal the impact of the endosymbiont Midichloria mitochondrii on the host mitochondria
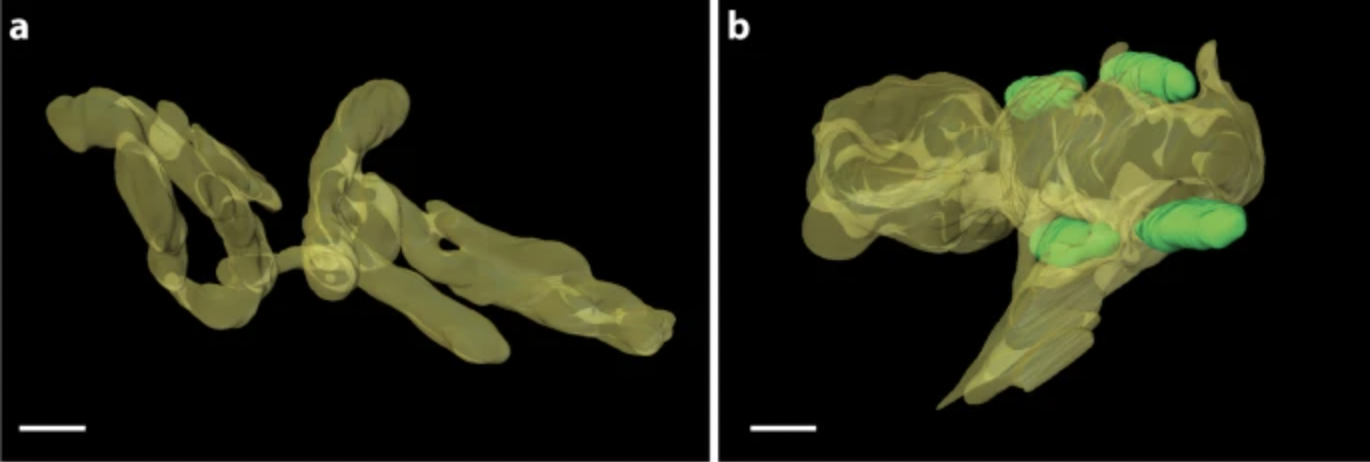
Congratulations to Dr. Zerrin Uzum (Regenerative Medicine Core) for being a first author on this Nature Communications paper. Dr. Uzum collaborated with researchers from ASU's School of Life Sciences and Instuiut Pasture, France.
How endosymbiont Midichloria mitochondrii impact host.
Age and Hormonal Stimulation Affect Tyramine Enrichment and Smooth Muscle Modulation within the Male Mouse Reproductive System
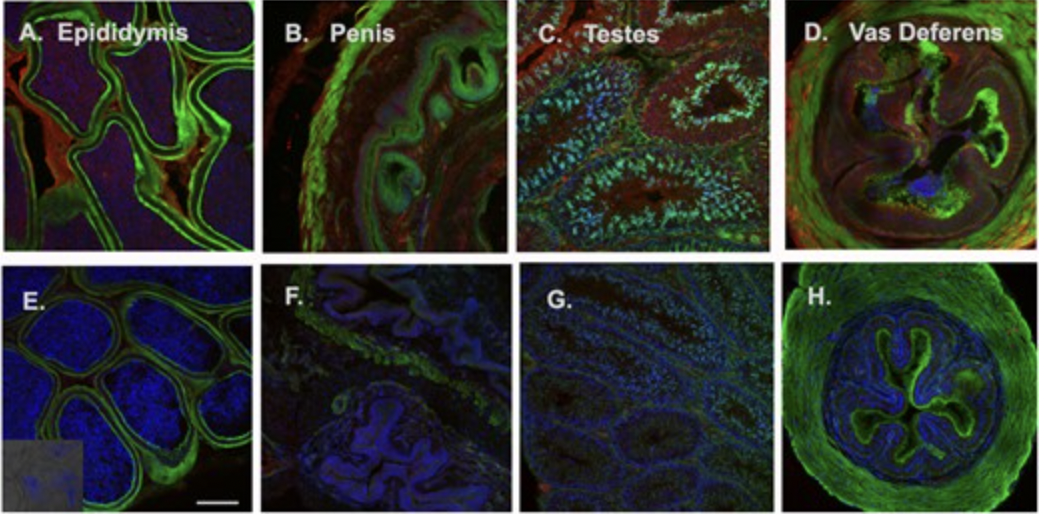
Congratulations to recent ASU Master's degree recipient and Histology Core Manager, Dr. Page Baluch, Assistant Director, Research Scientist and Regenerative Medicine Core Manager on their recent publication in Microscopy and microanalysis.

